Flow of Fluids: Newtonian and Non-Newtonian Fluids
Rheology is the term derived from the Greek word “rheo” meaning “to flow” and “logia” meaning “study of science.” Collectively, rheology is described as the science of flow of fluids and deformation of solids under applied forces.
In simple words, RHEOLOGY is the study of flow of fluids.
Rheology is an important factor for consideration in:
- Selection of suitable or proper machinery and process variable i.e. mixing, transferring liquids, filling, pouring etc. which are involved in manufacturing of pharmaceuticals.
- It affects any formulations dispensing i.e. extrusion of pastes, flow of fluids from syringes and needles, pouring certain doses from containers etc.
- Stability of preparations, storage conditions because temperature and other physical factors affects viscosity and rheological properties.
- Rheology also affects the bio-availability of drugs from formulations, as the rheologic properties affects the retention time at any specific site of biological systems.
On the basis of rheological and deformational properties the materials are classified into two types of systems:
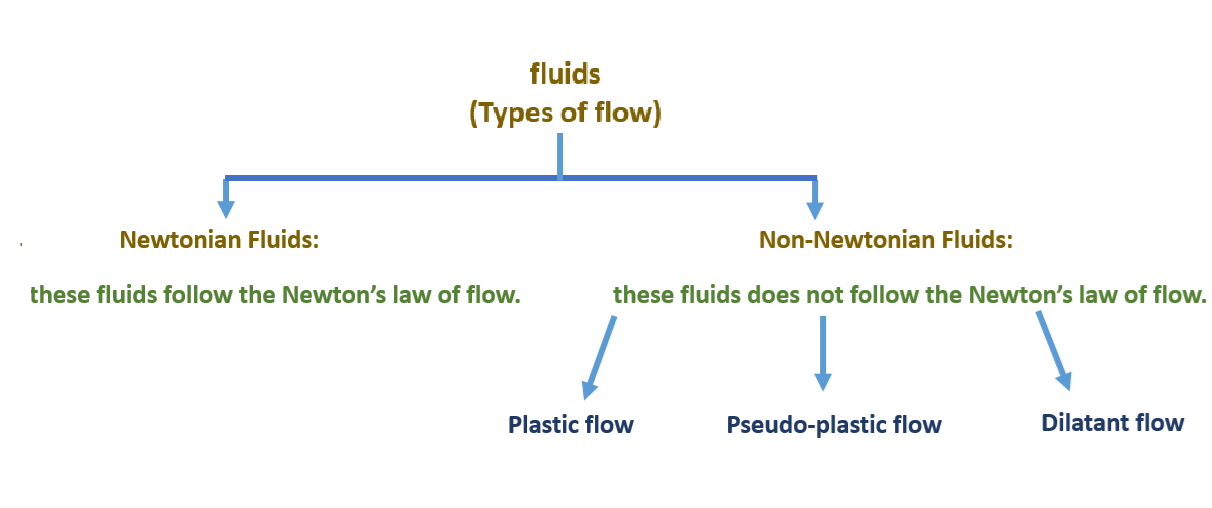
Newtonian Fluids
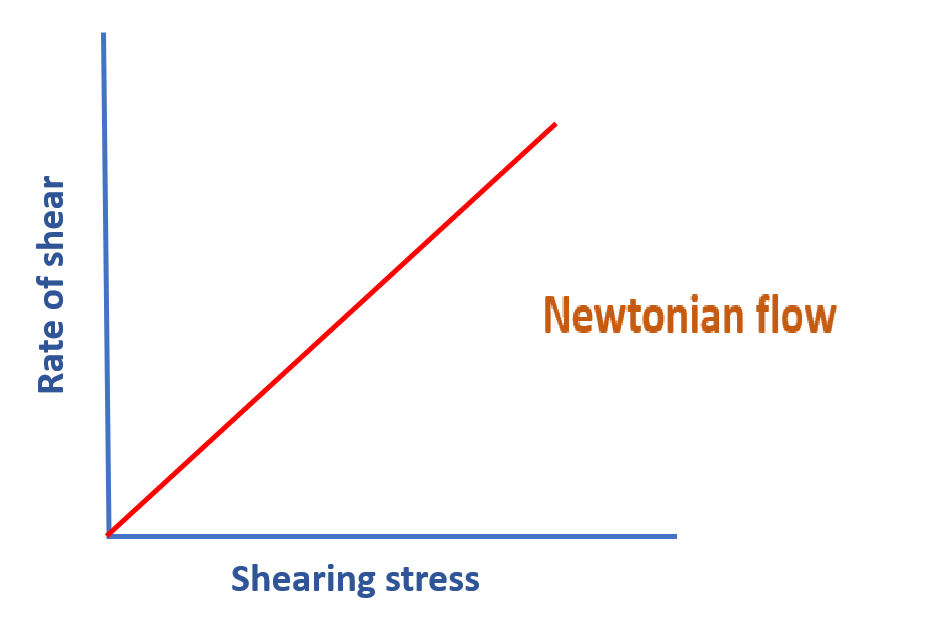
All material which follow the Newton’s law of flow are called Newtonian fluids. A per the Newton’s law of flow “the rate of shearing is directly proportional to shearing stress”.
Shearing Stress: the force per unit area (F/A), that is required to produce shearing or flow in any liquid is called shearing stress. Rate of Shearing: The bulk of liquid or any material is consider as multi-layered system. Each layer is move with different velocity because of friction between layers i.e. viscosity. Thus the difference in velocity (dv) between two layers at the distance of (dr) is called rate of shearing.
Thus, the rate of shearing (movement in material) is directly proportional to the shearing stress.
Plastic Flow
This is a Non-Newtonian type of flow and the materials which show plastic flow are also called “Bingham Bodies” on the name of scientist.
As in Newtonian system, the material show shearing as the shearing stress is applied. But the material showing plastic flow does not start to flow or move until a specific threshold of shear is not applied. More simply plastic flow systems require certain threshold of shear stress to become in the state of movement. That minimum force is called yield value. Below yield value, there is no shearing in fluid. This occurs because the molecules are attached together with Van der Walls force and certain threshold of power is required to break these attraction force and bring the molecules in motion or in the state of shear. Once the fluid start to flow, it follows Newtonian law of flow (or become Newtonian system).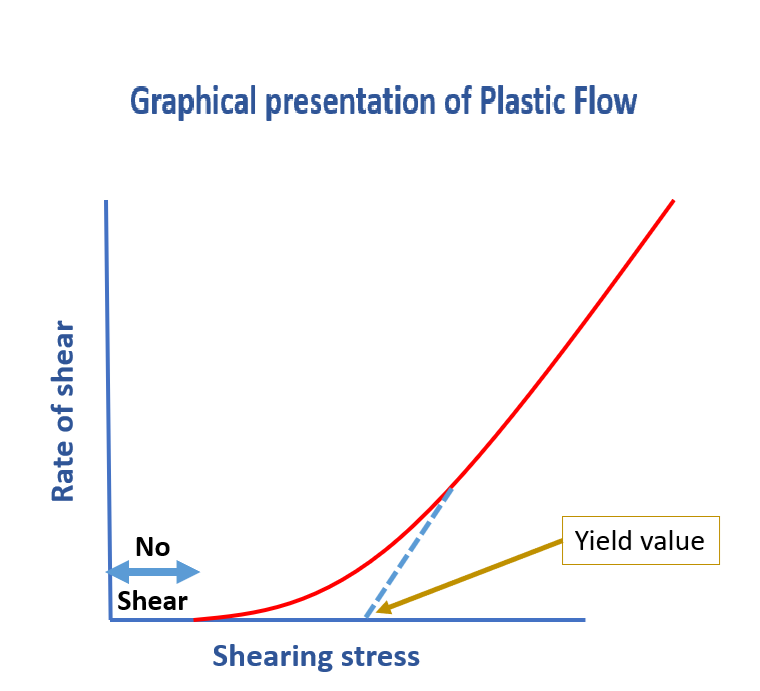
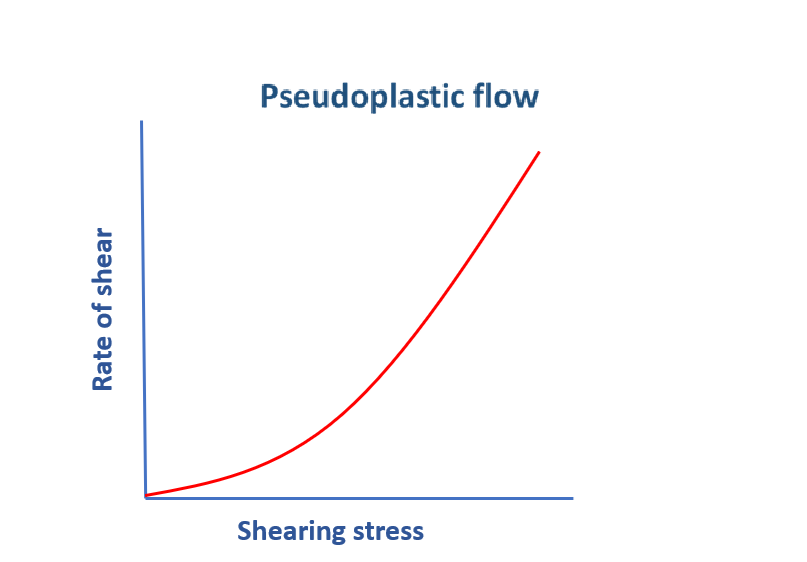
Pseudoplastic Flow
The viscosity of pseudoplastic substances decreases with increasing the rate of shear. Thus this kind of system are called “shear thinning systems”.
Generally long chain polymeric substances show this kind of flow property. The explanation of this as,- at starting or when very low shearing stress is applied, the polymeric molecules are in disarranged condition,
- but as the shearing stress gets increase, these longer molecules gets themselves arrange in their long axis in the direction of flow.
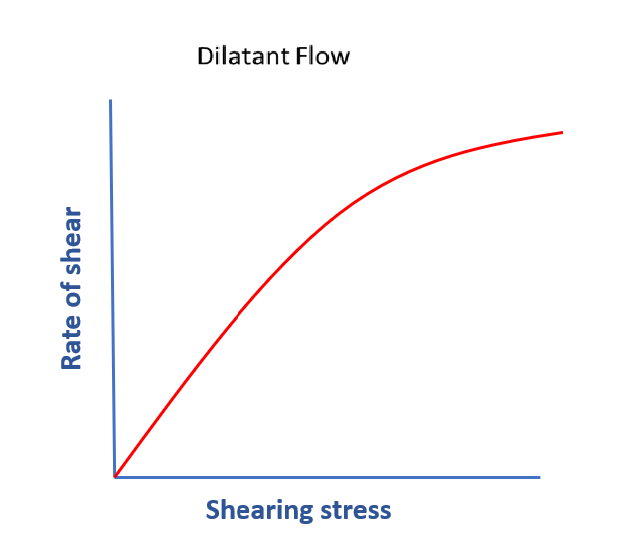
Dilatant Flow
These are also called shear thickening systems, because with the increased shearing stress, the system become more viscous or thick or the system show increase in resistance between layers of fluid. These kinds of system usually increase their volume when gets sheared, hence called dilatant.
The explanation of this kind of flow is- -at the resting condition, the particles are closely packed with lesser void space between them.
- In shearing condition, the space between particles gets increased and the system gets expands or dilates.
Example: Corn starch suspension in water.
Kinematic Viscosity
Kinematic viscosity is the ratio of dynamic viscosity to the density of a fluid. It measures a fluid’s viscosity when movement occurs due to gravity and no external force is applied.
The formula for this, is:
