Coating of Tablets — Overview
What is coating?
Coating is a process by which an essentially dry, outer layer of coating material is applied to the surface of a dosage form for some specific benefits like:
- Making the medicine look different or easy to identify.
- Protecting the drug from moisture, light, or air.
- Masking bad taste or smell.
- Controlling how fast or where the medicine is released in the body.
Objectives of Tablet coatings
- Coating provides a means of protection to the drug substance (active pharmaceutical ingredient), incorporated in tablet formulation from the external environment, particularly light and moisture, and thus potentially improve the product stability.
- Masking the taste of drug substances that may be bitter or otherwise unpleasant.
- Improving the ease of swallowing. (Coated tablets are considered by patients to be somewhat easier to swallow than uncoated tablets).
- Coating enhances product appearance and assist in brand recognition.
- Coloured coating on tablets facilitates the rapid identification of a product by the manufacturer, by the dispensing pharmacist and by the patient.
- Coating imparts modified-release characteristics that allow the drug to be delivered in a more effective and controlled manner.
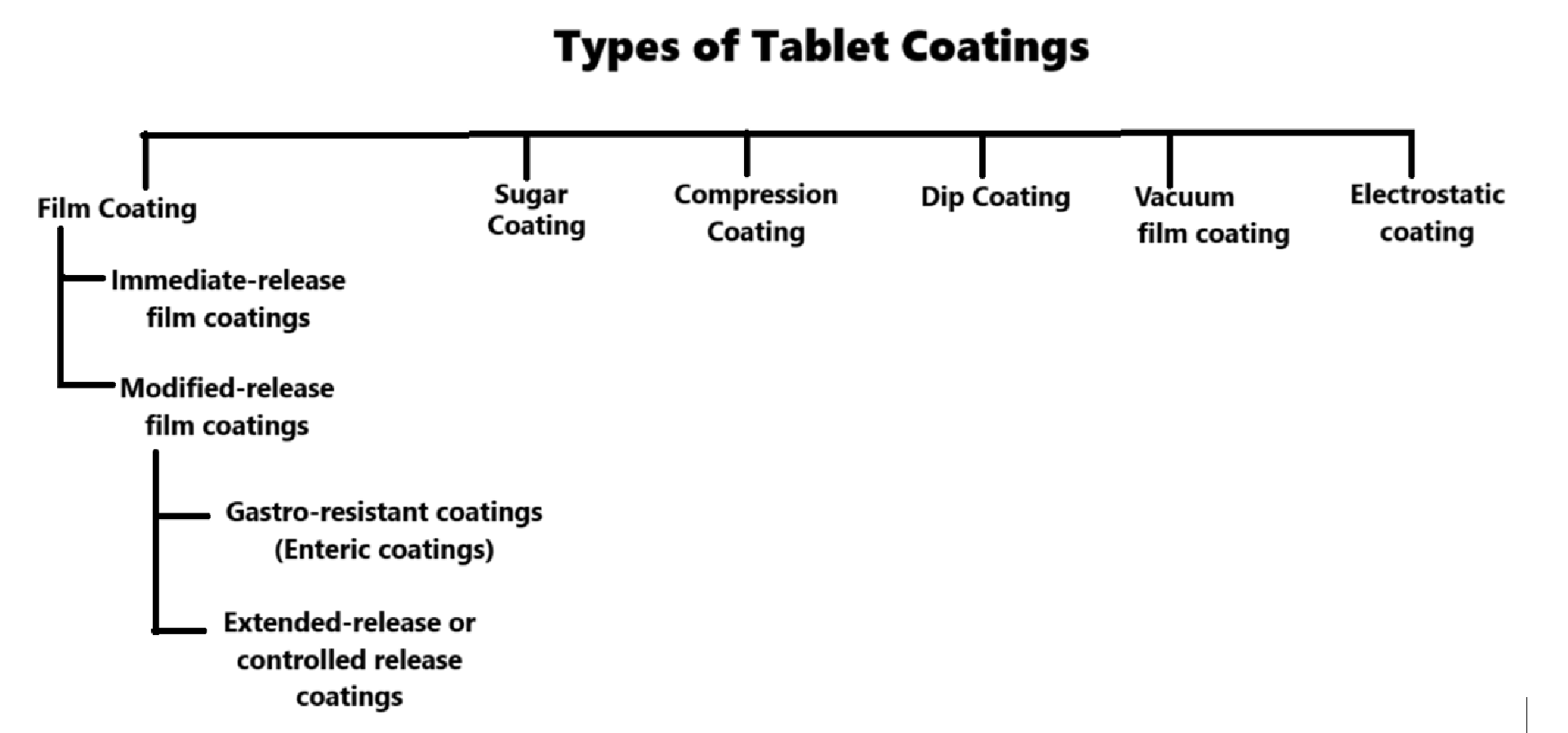
Types of Tablet coatings
Some generally used processes for tablet coating are:
1. Sugar Coating
It involves the successive application of sucrose-based coating formulations by pouring a sugar syrup, usually coloured, onto a bed of pre-varnished tablet cores rotating in a steel or copper pan into which warm air was blown.
The water evaporates from the syrup, leaving a thick sugar layer around each tablet. Sugar coats are often shiny and highly coloured. Sugar Coating is a traditional method for taste masking and aesthetic improvement. Sugar coating provides- Protection to the tablet,
- Masks the taste of the drug, and
- Enhances the aesthetic appearance,
- Making it more palatable.
Materials: sucrose, corn starch, gelatine, gum Arabic, etc.
2. Film Coating
Film coating involves the deposition, usually by the spraying of a liquid coating system, of a thin film of a polymer-based formulation onto the surface of a tablet.
Types of film coatings based on drug release characteristics.(a) Immediate-release film coatings
These types of coating are also known as ‘non-functional coatings. these coating has no measurable effect on biopharmaceutical properties i.e. drug release and its bioavailability. Immediate-release coatings are usually readily soluble in water. The term “non-functional” simply means they do not delay or control drug release.
The drug becomes available for absorption almost as soon as the tablet breaks apart. The name is a bit misleading because the coating does have functions, just not in controlling drug release. Once swallowed, the non-functional film Coating material, which is water-soluble gets dissolve within a few minutes in the stomach or swell quickly in gastric fluids and expose the core tablet for disintegration, dissolution and drug release. There is no drug release control mechanism.Polymers used: Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose (HPMC), Methylhydroxy ethyle cellulose, Ethyle cellulose, Hydroxypropyl Cellulose, Povidone, Sodium carboxymethyl Cellulose, Polyethyle Glycol
(b) Modified-release film coatings
These types of coating are also known as ‘functional’ coatings. These may be further categorized as either delayed-release (gastro-resistant) or extended-release coatings.
Gastro-resistant (enteric) coatings: are only soluble in water at pH values in excess of 5–6 and are intended to either protect the acid labile drugs form the degradation in the stomach, or to prevent the release of the drug in the stomach (in the case of drugs that are gastric irritants). Polymer used in this coating are: Cellulose acetate phthalate (CAP), Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose phthalate (HPMCP), Polyvinyl acetate phthalate (PVAP), Methacrylic acid copolymers (e.g., Eudragit® L100, S100) .
Extended-release coatings: are insoluble in water. They are designed to ensure that the drug is released in a consistent manner over a relatively long period of time (typically 6 hr. to 12 hr.) and thus reduce the number of doses that a patient needs to take in each 24-hour period. Additionally, extended-release film coatings are used to modify drug release in such a way that desired therapeutic benefits can more easily be achieved and thus drug efficacy can be improved. Polymer used in this coating are: Ethyl cellulose (EC), Polyvinyl acetate (PVAc), Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose (HPMC).
3. Compression Coating
It involves the compaction of granular material around a preformed tablet core using specially designed tableting equipment. Compression coating differs radically from film coating and sugar coating. The process involves the compaction of granular material around preformed tablet cores using specially designed tableting equipment.
Compression coating is essentially a dry process (although the coating formulation may have been produced by a wet-granulation process). Tablet cores are first prepared and then mechanically transferred, to another machine having slightly larger die that has been partially filled with the coating powder. The tablet core is positioned centrally into this partially filled die, more coating powder is added on top of the core and the whole composite mass undergoes a second compaction event. compression coating has been used to separate incompatible materials (one contained in the tablet core and the second contained in the coating). Compression coating is a mechanically complex process that requires careful formulation and processing of the coating layer.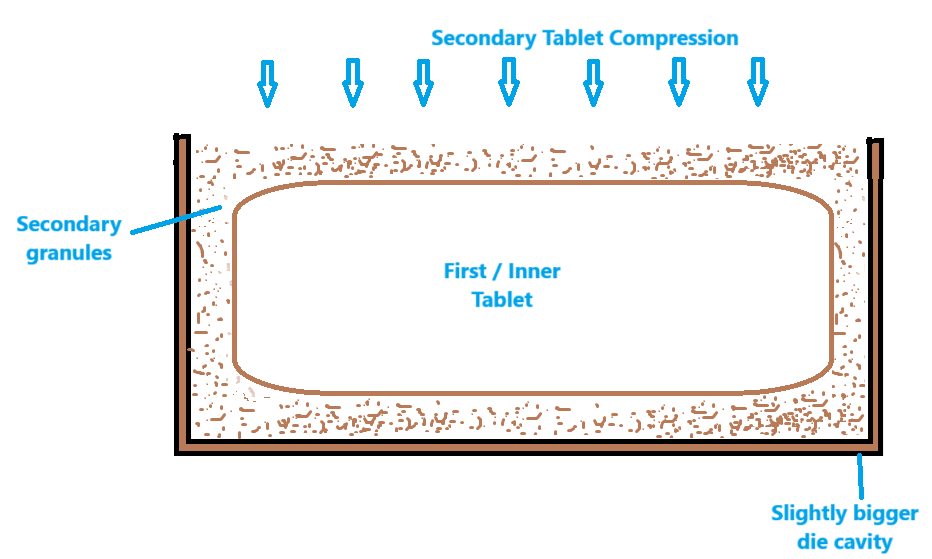
4. Electrostatic coating
Electrostatic coating is a method of applying coating to conductive substrates (Tablets). The coating particles (powder or spray droplets) are given an electric charge using a spray gun or powder applicator. Tablets may be placed on a conductive surface or exposed to opposite charges. Charged particles move toward the tablets and coat their surface evenly. Then Heat, UV light, or other methods fix the coating. Complete and uniform coating of tablet along with corners is properly achieved. Mostly used for dry powder coating of tablets, especially useful for moisture sensitive drugs.
5. Dip Coating
Coating is applied to the tablet cores by dipping them into the coating liquid. The wet tablets are dried in a coating pan, dipping and drying steps may be repeated several times to obtain the desired coating. This dip coating process lacks speed, versatility and reliability of the spray coating techniques.
6. Vacuum Film Coating
Vacuum film coating is a specialized tablet coating method carried out inside a vacuum chamber. Instead of coating in open air, the process happens under reduced pressure to improve coating efficiency, reduce solvent use, and produce high-quality films. In the sealed baffled pan, the tablets are placed and the nitrogen is used to displace the air in the pan before the desired vacuum level is obtained. The airless spray system is used to apply coating solution. The evaporation is caused by the heated pan and the vapours are removed by the vacuum system.
because the chamber is under vacuum, Solvent evaporates faster and less heat is required and coating spreads more evenly. This technique is specially designed for moisture and heat sensitive drugs, and ot can also used for producing enteric or sustained release tablets.Comparison: Sugar Coated vs Film Coated Tablets
| Features | Sugar Coated Tablets | Film Coated Tablets |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Glossy, smooth, often brightly coloured | Thin, matte, or semi-gloss finish. Usually not as shiny as sugar coat types |
| Weight gain after coating | 30–50% | 2–3% |
| Printing | Sugar-coated tablets, with their thicker, multi-layered coating, can be more challenging to print. | Film coating provides a smooth, uniform surface that is well-suited for printing logos, markings, and other identifying information. |
| Shape | Bulky and slightly oval or biconvex due to multiple layers | Film coated tablets have thinner layer over them, which does not alter the shape or size of the tablet significantly. |